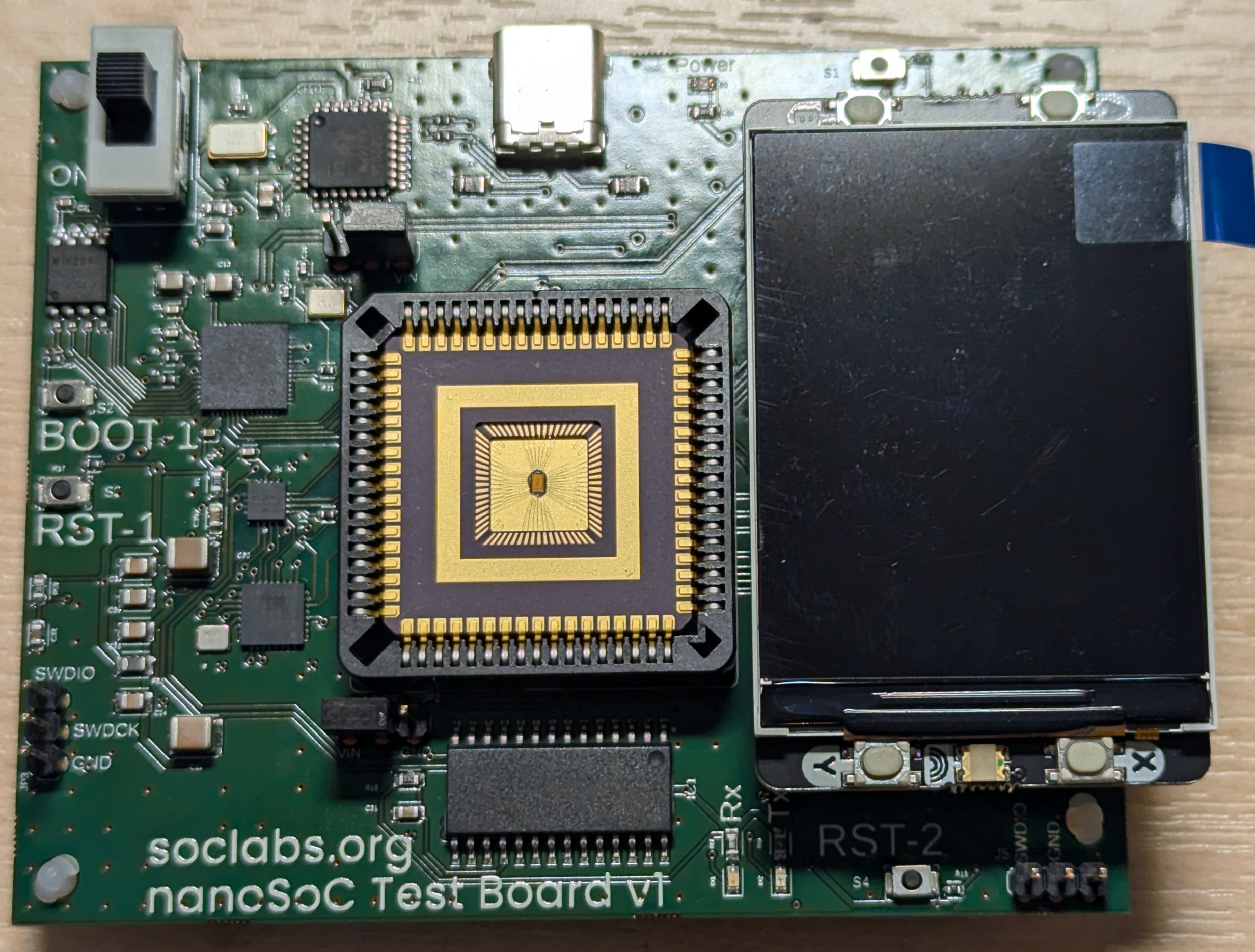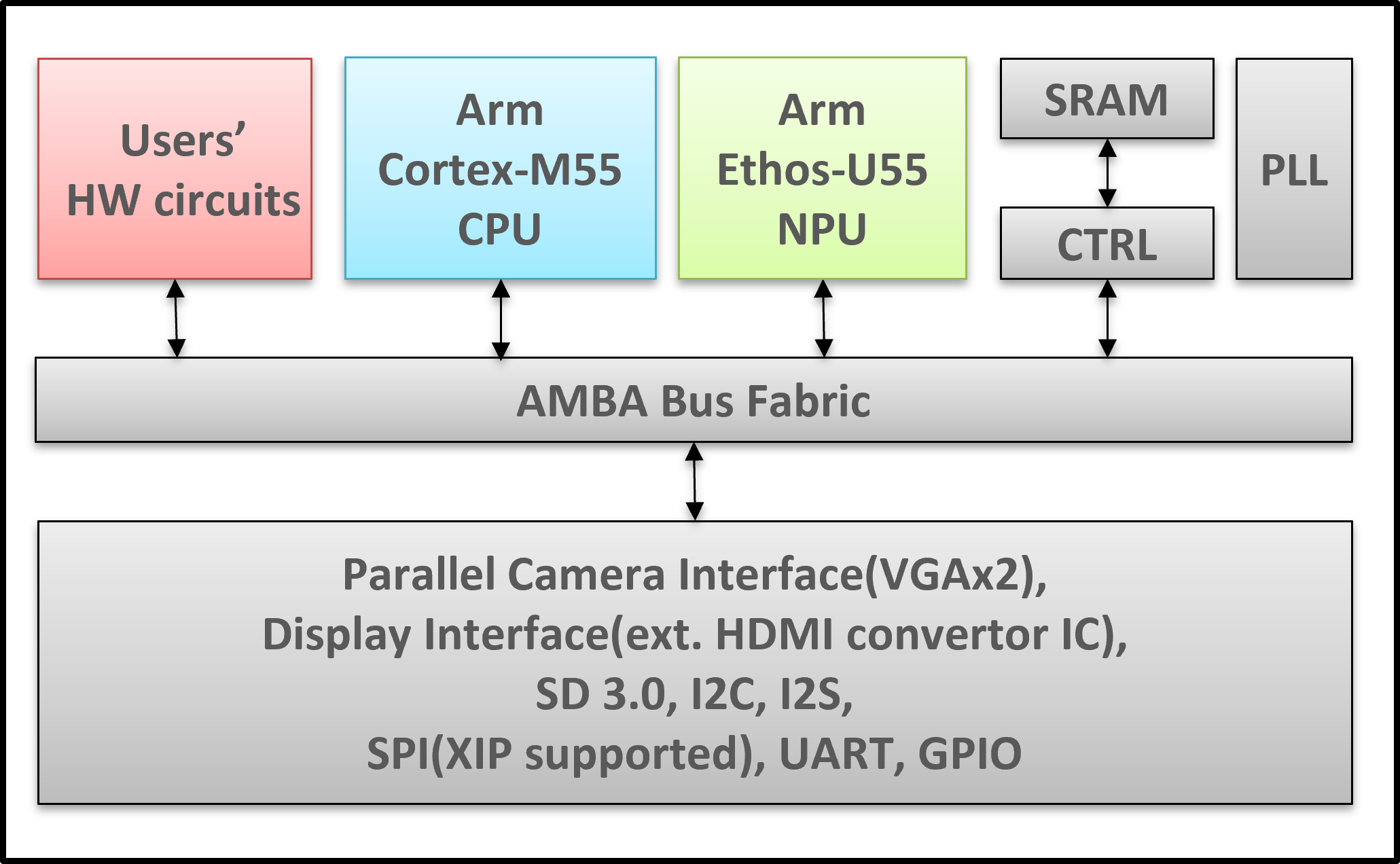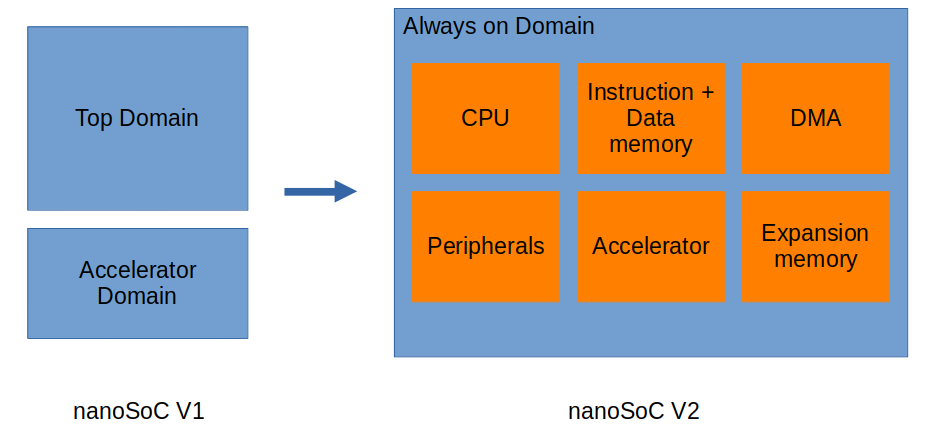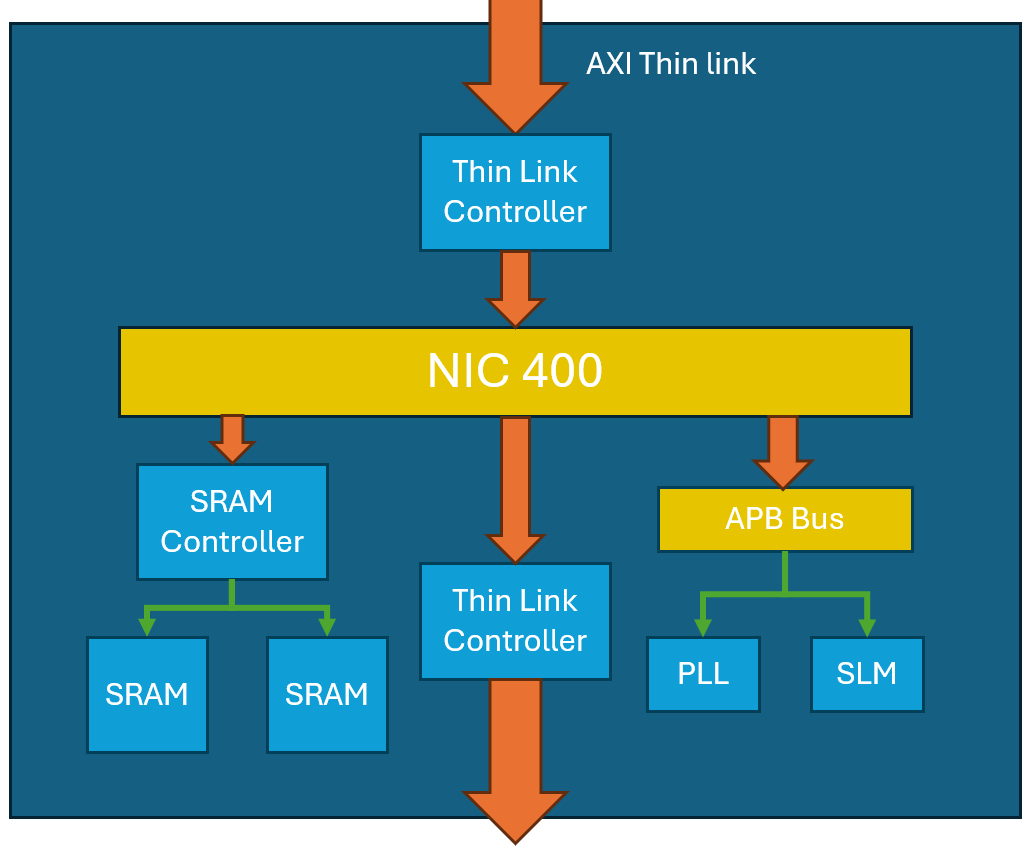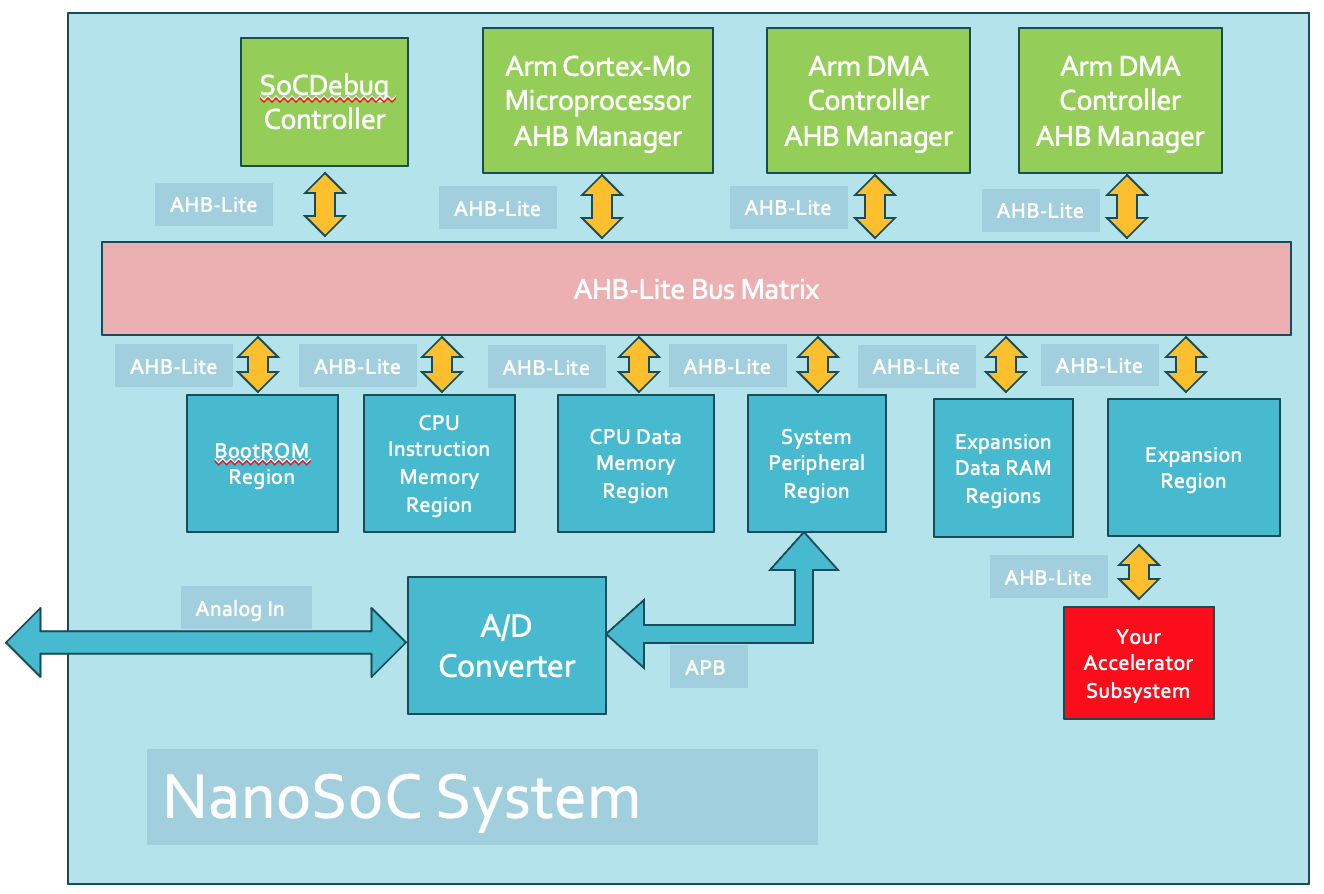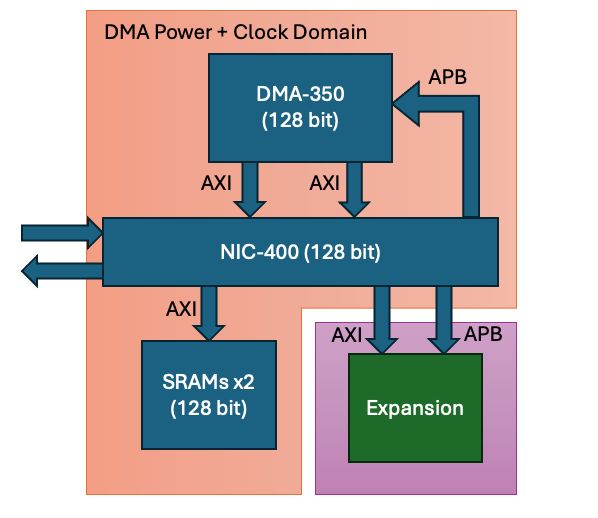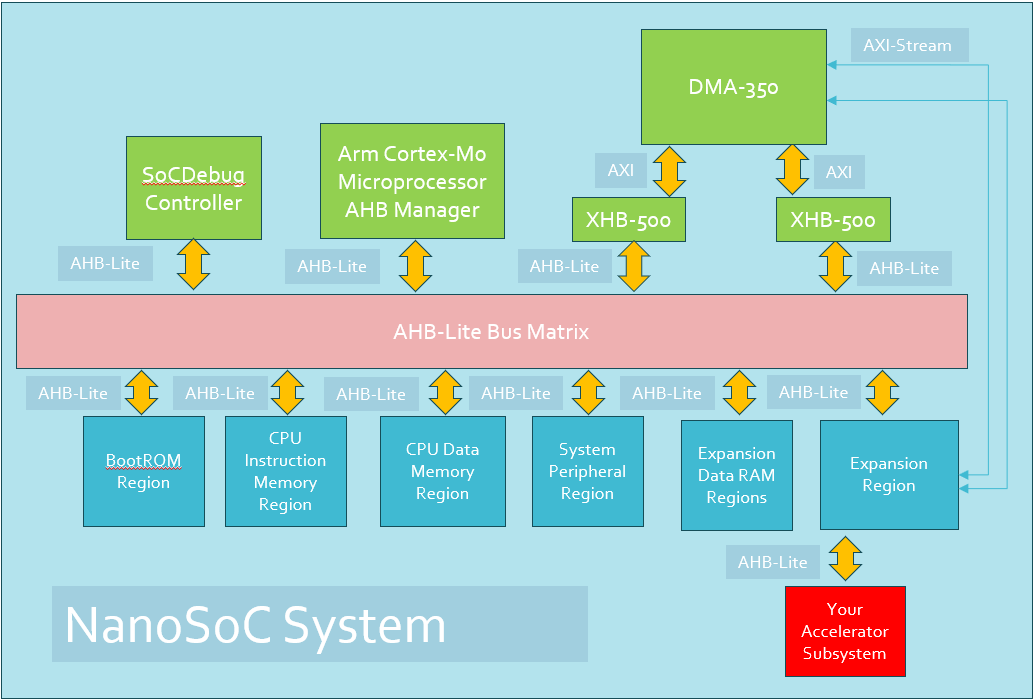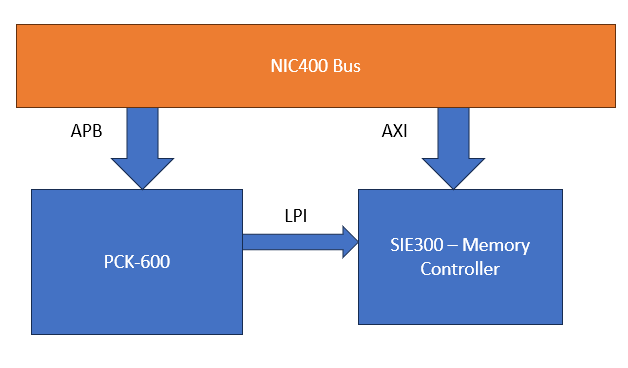
The PCK600 Arm IP provides components to allow a power control infrastructure to be distributed in a SoC in order to make a design energy efficient. Arm provide the IP as part of their Power Control System Architecture that can be used to control the power states of various parts of the system. This control of the power infrastructure is achieved through the use of the Power Policy Unit (PPU). This unit has an APB interface to allow for software control, and some low power interfaces that can connect to the power controllable IP within the system.
 Daniel Newbrook
Daniel Newbrook
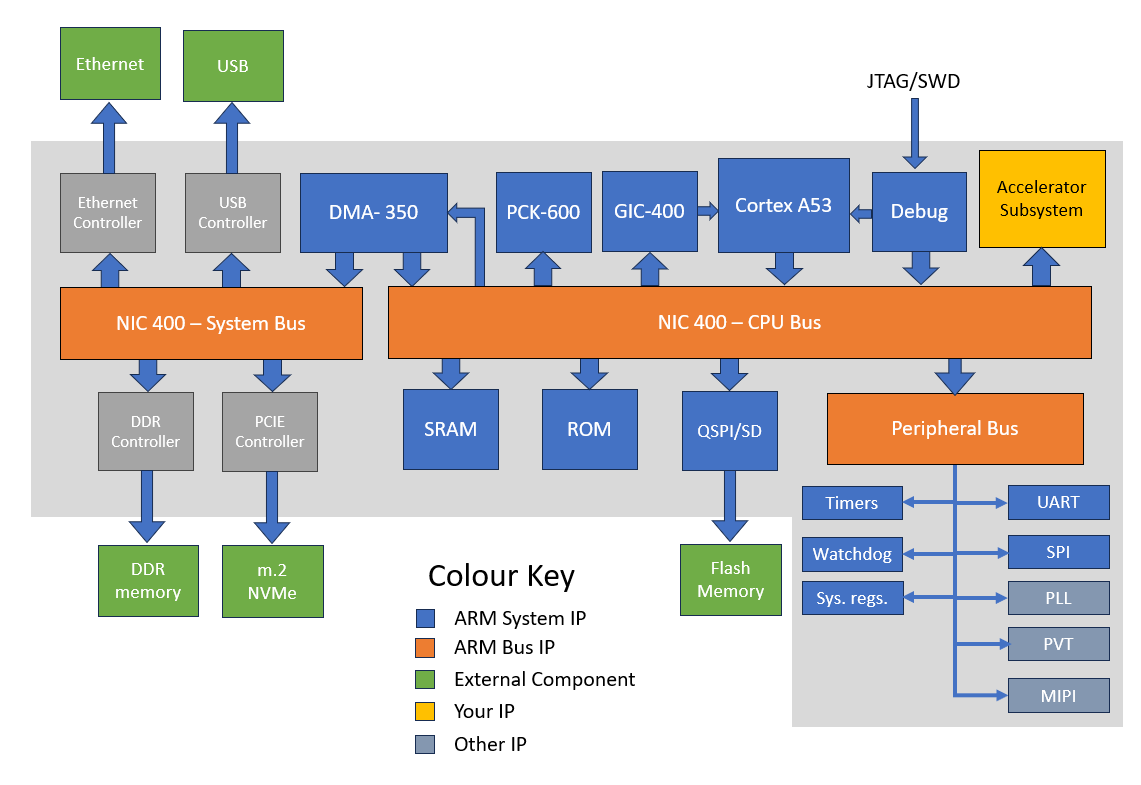
 David Flynn
David Flynn